Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
What is Remote Desktop Services (RDS)?
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is an umbrella term for features of Microsoft Windows Server that allow users to remotely access graphical desktops and Windows applications.
Users can access desktops and applications -- also known as Microsoft Azure -- from various types of client applications and devices, including non-Windows devices, via Microsoft's remote desktop protocol (RDP).
Remote Desktop Services components
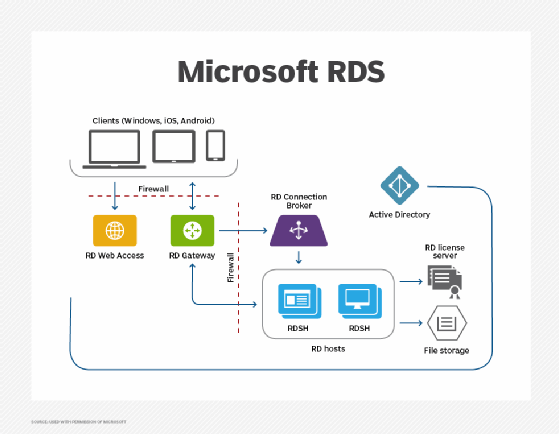
IT can implement Remote Desktop Services using multiple instances of Windows Server performing various roles.
The primary workload role, hosting Windows desktops and applications, is Remote Desktop Session Host (RDSH). RDSH contains session-based sharing capabilities that allow multiple users to access desktops and applications simultaneously on a single instance of Windows Server.
Remote Desktop Services infrastructure roles that are implemented in Windows Server include RD Connection Broker, RD Gateway, RD Licensing and RD Web Access.
Microsoft provides Remote Desktop clients for Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS, Apple iOS, Google Android and HTML5-capable browsers.
Remote Desktop Services evolution
Competing products such as Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops and VMware Horizon use the RDSH server role. Other products can provide their own brokers, display protocols, clients and management infrastructure.
Remote Desktop Services supports virtualized graphics processing units (GPUs) to enable graphically intensive applications.
IT can install Remote Desktop Services on premises, in public clouds on top of infrastructure as a service (IaaS) or in hybrid deployments.
Azure Virtual Desktop
In 2017, Microsoft announced a preview of new Azure-based infrastructure options for Remote Desktop Services under Remote Desktop modern infrastructure (RDmi). The company provided infrastructure roles for RD Connection Broker, RD Web and RD Gateway as Azure Web App services, instead of individual servers. RDmi used Azure Active Directory for authentication, and workloads -- such as RDSH servers -- had to run in Azure. RDmi was an easier way to enable multi-tenant RDS deployments.
Subsequently, in 2018, Microsoft announced that it would use RDmi for a new cloud-based desktop and application offering called Windows Virtual Desktop, which was later renamed Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD). AVD is a desktop as a service (DaaS) product that offers virtual desktop and application access through Microsoft Azure's cloud infrastructure.
Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2022
Remote Desktop Services is available in Windows Server 2019 and 2022. Since the introduction of Windows Server 2019, however, some features are restricted. Windows Server Desktop Experience and RDSH do not include newer features such as Microsoft Cortana, the Microsoft Store and the Xbox app and services.








