
remote wipe
What is a remote wipe?
Remote wipe is a security feature that allows a network administrator or device owner to send a command that remotely deletes data from a computing device. It's primarily used to erase data on a device that has been lost or stolen, so the data won't be compromised if it falls into the wrong hands. It's also used to remove data from a device that has changed owners or administrators and can't be accessed physically to remove data.
Remote wipes are mainly used for mobile devices such as smartphones or laptops. Remote wipes can help a user keep data out of the hands of others if they lose their device, or as a mobile device management (MDM) precaution in an organization.
Remote wipe contrasts with local wipe -- also called auto wipe -- a data security feature that deletes all data on a mobile device after a pre-specified number of failed login attempts or after a device moves outside of a defined physical boundary.
How does a remote wipe work?
Once a device is known to be lost or stolen, the device user or administrator has options for wiping the device. What remote wipe specifically accomplishes depends on the device, its specific operating system version and the third-party MDM software installed on it.
A remote wipe can delete data in selected folders, repeatedly overwrite stored data to prevent recovery using a forensic image, return the device to factory settings or remove all programming on the device -- meaning that it's no longer of any use to anyone.
For a remote wipe to work, a device needs to be powered on and connected to a network so it can receive the communication from the software commanding it to be wiped. A user attempting to remotely wipe their missing device can run into problems if the device is rebooted during the process, if the device is on airplane mode or if connectivity to the device is somehow otherwise impeded.
A remote wipe is used in both enterprise devices that contain company data and personal devices that hold personal data. Ideal software and methods of remote wipe vary depending on whether the device is for personal or enterprise use. For example, if an organization has a bring your own device (BYOD) policy, some MDM software has an enterprise wipe setting that only deletes the associated data installed by the organization -- meaning the user's personal data is kept intact. This method can be used if an employee loses their device, or if they end their employment with the company.
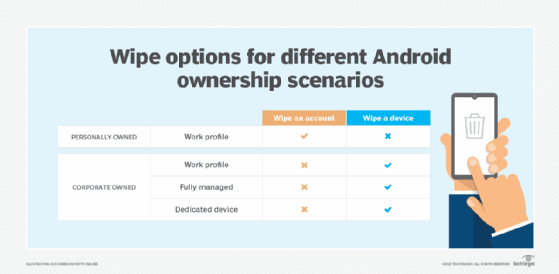
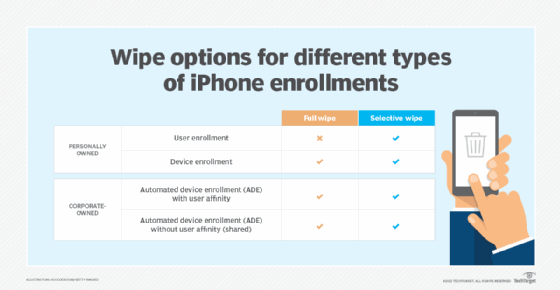
Who offers remote wipe?
In the enterprise, remote wipe capabilities are available natively on most smartphones and tablets through Exchange ActiveSync, which synchronizes access to email, calendar, contacts and tasks from the organization's Microsoft Exchange Server. Other enterprise-centric MDM applications -- also known as enterprise mobility management (EMM) software -- that offer remote wipe include the following:
- AirDroid Business is an MDM remote wipe software that supports Android, iOS, Windows and macOS devices. It performs remote wipes, locks device screens and files, forces password resets and automatically factory resets a device.
- Apple Business Manager is a web-based platform that does remote wipes of iOS, iPadOS and macOS devices. Files are still recoverable up to 30 days after wiping.
- Google Workspace is primarily used in enterprises and schools and enables IT admins within these organizations to remotely wipe devices.
- Knox Manage is an MDM tool for organizations to remote wipe Samsung devices. This tool has a restore option and can also track lost devices.
- VMware Workspace One helps IT departments manage enterprise devices by securing and enforcing policies on those devices. It includes an Enterprise Wipe feature that can remove all corporate access and content without touching personal files and settings.
MDM products also offer this technology as consumer-focused apps. Examples include the following:
- Android Device Manager is a consumer-focused MDM application with a remote wipe feature. The device manager, also known as Find My Device, allows users to wipe their Android phone, tablet or smartwatch, as well as remotely lock or call the device. The device manager, while not automatically installed on the Android platform, is available for download in the Google Play App store.
- Apple Find My and Find Devices on iCloud.com can help users track their Apple devices even if they're offline or powered off. This app allows users to wipe their phones, as well as call the device.
- Prey is a third-party app with free and paid options for both consumers and enterprises. It enables users to manage and wipe devices across platforms. Prey can monitor laptops and PCs as well as mobile phones and tablets.
- Trend Micro Lost Device Protection is available for both Android and iOS. It offers location and alarm features for both operating systems, and wipe and lock features for Android only.
Aside from MDM applications, there are also consumer-focused cloud applications that offer their own built-in wipe feature. For example, Dropbox allows users to wipe any Dropbox-related data from a compromised device with one click. This remote wipe option focuses on wiping the data provided by one application, as opposed to wiping data based on its location in the phone. Users who wipe data using a cloud-based application like Dropbox still have that data in their account, but it's removed from the device they've chosen to wipe.
Pros and cons of remote wiping
Benefits of remote wiping include the following:
- Improves overall security posture. Having the capacity to remote wipe a device improves an organization's ability to predict, prevent and respond to potential threats.
- Protects private data. Remote wiping helps protect an individual's private data by deleting it if the device is lost or stolen.
- Prevents potential or further data breaches. Wiping a lost or stolen device can help prevent sensitive data from reaching threat actors or could help stop a further breach if a cyber attack has already been launched on an organization.
- Works on multiple platforms. A remote wipe, depending on the software tool used, can be performed on Android, iOS, Windows or macOS for devices such as smartphones, tablets, smartwatches and laptops.
- Removes data from past employees. Remote wiping is a good method for deleting data off a former employee's laptop or phone.
- Wipes only business-related data. Employees don't have to worry about their personal data being deleted in a BYOB environment.
- Secures a device without a network connection. Some MDM tools can lock devices automatically if they don't connect to the network for a specified amount of time or send a push notification with a customized message to a device's lock screen.
Remote wipes do have some drawbacks as well. These typically include the following:
- Devices must remain online. The device must be connected over a network to receive the signal to start the wiping process. A device wipe can't initiate if the device is turned off.
- Remote wipes are interruptible. Data might not be successfully deleted if the device is rebooted during a wipe, and the amount of time it takes to wipe a device varies depending on the amount of data to erase.
- Data can still be recoverable from a remotely wiped device. If the available blocks aren't overwritten or rendered completely unreadable, the deleted data could still be retrievable.
- Remote wipes are only effective against known device loss or theft. Devices are typically wiped if the admin, employee or individual is aware their device has been lost or stolen.
Remote wipe best practices for businesses
The following best practices can help ensure an organization correctly manages the remote wipe process:
- Ensure mobile devices are powered on to receive the remote wipe signal.
- If employing a BYOD strategy, ensure the remote wipe tool supports an enterprise wipe setting to only delete company-related data and not an employee's personal data.
- Inform employees that only company-related data will be wiped in the case of a lost device. This helps lessen the chance an employee won't report a lost or stolen device.
- Educate employees on mobile security to help prevent lost or stolen devices.
- Use a mobile container to separate an employee's personal data from business data. This eases the process for IT admins in wiping only work profiles and business-related data.
- Monitor business service use on mobile devices. If a device hasn't accessed business data over a specified time period, it could indicate the device was lost or stolen.
Learn about other methods of mobile device security for businesses.






